Inductor
| This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |

A selection of low-value inductors
|
|
| Type | Passive |
|---|---|
| Working principle | Electromagnetic induction |
| First production | Michael Faraday (1831) |
| Electronic symbol | |
An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil. Energy is stored in a magnetic field in the coil as long as current flows. When the current flowing through an inductor changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces a voltage in the conductor, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. According to Lenz's law the direction of induced electromotive force (or "e.m.f.") is always such that it opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors always oppose a change in current, in the same way that a flywheel opposes a change in rotational velocity. Care should be taken not to confuse this with the resistance provided by a resistor.
An inductor is characterized by its inductance, the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current, which has units of henries (H). Inductors have values that typically range from 1 µH (10−6H) to 1 H. Many inductors have a magnetic core made of iron or ferrite inside the coil, which serves to increase the magnetic field and thus the inductance. Along with capacitors and resistors, inductors are one of the three passive linear circuit elements that make up electric circuits. Inductors are widely used in alternating current (AC) electronic equipment, particularly in radio equipment. They are used to block AC while allowing DC to pass; inductors designed for this purpose are called chokes. They are also used in electronic filters to separate signals of different frequencies, and in combination with capacitors to make tuned circuits, used to tune radio and TV receivers.
Contents
Overview[edit]
Inductance (L) results from the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor; the electric current through the conductor creates a magnetic flux. Mathematically speaking, inductance is determined by how much magnetic flux φ through the circuit is created by a given current i[1][2][3][4]
 (1)
(1)
Inductors that have ferromagnetic cores are nonlinear; the inductance changes with the current, in this more general case inductance is defined as
Any wire or other conductor will generate a magnetic field when current flows through it, so every conductor has some inductance. The inductance of a circuit depends on the geometry of the current path as well as the magnetic permeability of nearby materials. An inductor is a component consisting of a wire or other conductor shaped to increase the magnetic flux through the circuit, usually in the shape of a coil or helix. Winding the wire into a coil increases the number of times the magnetic flux lines link the circuit, increasing the field and thus the inductance. The more turns, the higher the inductance. The inductance also depends on the shape of the coil, separation of the turns, and many other factors. By adding a "magnetic core" made of a ferromagnetic material like iron inside the coil, the magnetizing field from the coil will induce magnetization in the material, increasing the magnetic flux. The high permeability of a ferromagnetic core can increase the inductance of a coil by a factor of several thousand over what it would be without it.
Constitutive equation[edit]
Any change in the current through an inductor creates a changing flux, inducing a voltage across the inductor. By Faraday's law of induction, the voltage induced by any change in magnetic flux through the circuit is[4]
From (1) above[4]
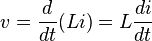 (2)
(2)
So inductance is also a measure of the amount of electromotive force (voltage) generated for a given rate of change of current. For example, an inductor with an inductance of 1 henry produces an EMF of 1 volt when the current through the inductor changes at the rate of 1 ampere per second. This is usually taken to be the constitutive relation (defining equation) of the inductor.
The dual of the inductor is the capacitor, which stores energy in an electric field rather than a magnetic field. Its current-voltage relation is obtained by exchanging current and voltage in the inductor equations and replacing L with the capacitance C.
Lenz's law[edit]
The polarity (direction) of the induced voltage is given by Lenz's law, which states that it will be such as to oppose the change in current. For example, if the current through an inductor is increasing, the induced voltage will be positive at the terminal through which the current enters and negative at the terminal through which it leaves, tending to oppose the additional current. The energy from the external circuit necessary to overcome this potential "hill" is being stored in the magnetic field of the inductor; the inductor is said to be "charging" or "energizing". If the current is decreasing, the induced voltage will be negative at the terminal through which the current enters and positive at the terminal through which it leaves, tending to maintain the current. Energy from the magnetic field is being returned to the circuit; the inductor is said to be "discharging".
Ideal and real inductors[edit]
In circuit theory, inductors are idealized as obeying the mathematical relation (2) above precisely. An "ideal inductor" has inductance, but no resistance or capacitance, and does not dissipate or radiate energy. However real inductors have side effects which cause their behavior to depart from this simple model. They have resistance (due to the resistance of the wire and energy losses in core material), and parasitic capacitance (due to the electric field between the turns of wire which are at slightly different potentials). At high frequencies the capacitance begins to affect the inductor's behavior; at some frequency, real inductors behave as resonant circuits, becoming self-resonant. Above the resonant frequency the capacitive reactance becomes the dominant part of the impedance. At higher frequencies, resistive losses in the windings increase due to skin effect and proximity effect.
Inductors with ferromagnetic cores have additional energy losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents in the core, which increase with frequency. At high currents, iron core inductors also show gradual departure from ideal behavior due to nonlinearity caused by magnetic saturation of the core. An inductor may radiate electromagnetic energy into surrounding space and circuits, and may absorb electromagnetic emissions from other circuits, causing electromagnetic interference (EMI). Real-world inductor applications may consider these parasitic parameters as important as the inductance.
Applications[edit]


Inductors are used extensively in analog circuits and signal processing. Applications range from the use of large inductors in power supplies, which in conjunction with filter capacitors remove residual hums known as the mains hum or other fluctuations from the direct current output, to the small inductance of the ferrite bead or torus installed around a cable to prevent radio frequency interference from being transmitted down the wire. Inductors are used as the energy storage device in many switched-mode power supplies to produce DC current. The inductor supplies energy to the circuit to keep current flowing during the "off" switching periods.
An inductor connected to a capacitor forms a tuned circuit, which acts as a resonator for oscillating current. Tuned circuits are widely used in radio frequency equipment such as radio transmitters and receivers, as narrow bandpass filters to select a single frequency from a composite signal, and in electronic oscillators to generate sinusoidal signals.
Two (or more) inductors in proximity that have coupled magnetic flux (mutual inductance) form a transformer, which is a fundamental component of every electric utility power grid. The efficiency of a transformer may decrease as the frequency increases due to eddy currents in the core material and skin effect on the windings. The size of the core can be decreased at higher frequencies. For this reason, aircraft use 400 hertz alternating current rather than the usual 50 or 60 hertz, allowing a great saving in weight from the use of smaller transformers.[5]
Inductors are also employed in electrical transmission systems, where they are used to limit switching currents and fault currents. In this field, they are more commonly referred to as reactors.
Because inductors have complicated side effects (detailed below) which cause them to depart from ideal behavior, because they can radiate electromagnetic interference (EMI), and most of all because of their bulk which prevents them from being integrated on semiconductor chips, the use of inductors is declining in modern electronic devices, particularly compact portable devices. Real inductors are increasingly being replaced by active circuits such as the gyrator which can synthesize inductance using capacitors.
Inductor construction[edit]
An inductor usually consists of a coil of conducting material, typically insulated copper wire, wrapped around a core either of plastic or of a ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic) material; the latter is called an "iron core" inductor. The high permeability of the ferromagnetic core increases the magnetic field and confines it closely to the inductor, thereby increasing the inductance. Low frequency inductors are constructed like transformers, with cores of electrical steel laminated to prevent eddy currents. 'Soft' ferrites are widely used for cores above audio frequencies, since they do not cause the large energy losses at high frequencies that ordinary iron alloys do. Inductors come in many shapes. Most are constructed as enamel coated wire (magnet wire) wrapped around a ferrite bobbin with wire exposed on the outside, while some enclose the wire completely in ferrite and are referred to as "shielded". Some inductors have an adjustable core, which enables changing of the inductance. Inductors used to block very high frequencies are sometimes made by stringing a ferrite bead on a wire.
Small inductors can be etched directly onto a printed circuit board by laying out the trace in a spiral pattern. Some such planar inductors use a planar core.
Small value inductors can also be built on integrated circuits using the same processes that are used to make transistors. Aluminium interconnect is typically used, laid out in a spiral coil pattern. However, the small dimensions limit the inductance, and it is far more common to use a circuit called a "gyrator" that uses a capacitor and active components to behave similarly to an inductor.
Types of inductor[edit]
Air core inductor[edit]
The term air core coil describes an inductor that does not use a magnetic core made of a ferromagnetic material. The term refers to coils wound on plastic, ceramic, or other nonmagnetic forms, as well as those that have only air inside the windings. Air core coils have lower inductance than ferromagnetic core coils, but are often used at high frequencies because they are free from energy losses called core losses that occur in ferromagnetic cores, which increase with frequency. A side effect that can occur in air core coils in which the winding is not rigidly supported on a form is 'microphony': mechanical vibration of the windings can cause variations in the inductance.
Radio frequency inductor[edit]

At high frequencies, particularly radio frequencies (RF), inductors have higher resistance and other losses. In addition to causing power loss, in resonant circuits this can reduce the Q factor of the circuit, broadening the bandwidth. In RF inductors, which are mostly air core types, specialized construction techniques are used to minimize these losses. The losses are due to these effects:
- Skin effect: The resistance of a wire to high frequency current is higher than its resistance to direct current because of skin effect. Radio frequency alternating current does not penetrate far into the body of a conductor but travels along its surface. Therefore, in a solid wire, most of the cross sectional area of the wire is not used to conduct the current, which is in a narrow annulus on the surface. This effect increases the resistance of the wire in the coil, which may already have a relatively high resistance due to its length and small diameter.
- Proximity effect: Another similar effect that also increases the resistance of the wire at high frequencies is proximity effect, which occurs in parallel wires that lie close to each other. The individual magnetic field of adjacent turns induces eddy currents in the wire of the coil, which causes the current in the conductor to be concentrated in a thin strip on the side near the adjacent wire. Like skin effect, this reduces the effective cross-sectional area of the wire conducting current, increasing its resistance.
- Dielectric losses: The high frequency electric field near the conductors in a tank coil can cause the motion of polar molecules in nearby insulating materials, dissipating energy as heat. So coils used for tuned circuits are often not wound on coil forms but are suspended in air, supported by narrow plastic or ceramic strips.
- Parasitic capacitance: The capacitance between individual wire turns of the coil, called parasitic capacitance, does not cause energy losses but can change the behavior of the coil. Each turn of the coil is at a slightly different potential, so the electric field between neighboring turns stores charge on the wire, so the coil acts as if it has a capacitor in parallel with it. At a high enough frequency this capacitance can resonate with the inductance of the coil forming a tuned circuit, causing the coil to become self-resonant.
To reduce parasitic capacitance and proximity effect, high Q RF coils are constructed to avoid having many turns lying close together, parallel to one another. The windings of RF coils are often limited to a single layer, and the turns are spaced apart. To reduce resistance due to skin effect, in high-power inductors such as those used in transmitters the windings are sometimes made of a metal strip or tubing which has a larger surface area, and the surface is silver-plated.
- Basket-weave coils: To reduce proximity effect and parasitic capacitance, multilayer RF coils are wound in patterns in which successive turns are not parallel but crisscrossed at an angle; these are often called honeycomb or basket-weave coils. These are occasionally wound on a vertical insulating supports with dowels or slots, with the wire weaving in and out through the slots.
- Spiderweb coils: Another construction technique with similar advantages is flat spiral coils.These are often wound on a flat insulating support with radial spokes or slots, with the wire weaving in and out through the slots; these are called spiderweb coils. The form has an odd number of slots, so successive turns of the spiral lie on opposite sides of the form, increasing separation.
- Litz wire: To reduce skin effect losses, some coils are wound with a special type of radio frequency wire called litz wire. Instead of a single solid conductor, litz wire consists of a number of smaller wire strands that carry the current. Unlike ordinary stranded wire, the strands are insulated from each other, to prevent skin effect from forcing the current to the surface, and are twisted or braided together. The twist pattern ensures that each wire strand spends the same amount of its length on the outside of the wire bundle, so skin effect distributes the current equally between the strands, resulting in a larger cross-sectional conduction area than an equivalent single wire.
Ferromagnetic core inductor[edit]
Ferromagnetic-core or iron-core inductors use a magnetic core made of a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron or ferrite to increase the inductance. A magnetic core can increase the inductance of a coil by a factor of several thousand, by increasing the magnetic field due to its higher magnetic permeability. However the magnetic properties of the core material cause several side effects which alter the behavior of the inductor and require special construction:
- Core losses: A time-varying current in a ferromagnetic inductor, which causes a time-varying magnetic field in its core, causes energy losses in the core material that are dissipated as heat, due to two processes:
- Eddy currents: From Faraday's law of induction, the changing magnetic field can induce circulating loops of electric current in the conductive metal core. The energy in these currents is dissipated as heat in the resistance of the core material. The amount of energy lost increases with the area inside the loop of current.
- Hysteresis: Changing or reversing the magnetic field in the core also causes losses due to the motion of the tiny magnetic domains it is composed of. The energy loss is proportional to the area of the hysteresis loop in the BH graph of the core material. Materials with low coercivity have narrow hysteresis loops and so low hysteresis losses.
- For both of these processes, the energy loss per cycle of alternating current is constant, so core losses increase linearly with frequency. Online core loss calculators[10] are available to calculate the energy loss. Using inputs such as input voltage, output voltage, output current, frequency, ambient temperature, and inductance these calculators can predict the losses of the inductors core and AC/DC based on the operating condition of the circuit being used.[11]
- Nonlinearity: If the current through a ferromagnetic core coil is high enough that the magnetic core saturates, the inductance will not remain constant but will change with the current through the device. This is called nonlinearity and results in distortion of the signal. For example, audio signals can suffer intermodulation distortion in saturated inductors. To prevent this, in linear circuits the current through iron core inductors must be limited below the saturation level. Some laminated cores have a narrow air gap in them for this purpose, and powdered iron cores have a distributed air gap. This allows higher levels of magnetic flux and thus higher currents through the inductor before it saturates.[12]
Laminated core inductor[edit]
Low-frequency inductors are often made with laminated cores to prevent eddy currents, using construction similar to transformers. The core is made of stacks of thin steel sheets or laminations oriented parallel to the field, with an insulating coating on the surface. The insulation prevents eddy currents between the sheets, so any remaining currents must be within the cross sectional area of the individual laminations, reducing the area of the loop and thus reducing the energy losses greatly. The laminations are made of low-coercivity silicon steel, to reduce hysteresis losses.
Ferrite-core inductor[edit]
For higher frequencies, inductors are made with cores of ferrite. Ferrite is a ceramic ferrimagnetic material that is nonconductive, so eddy currents cannot flow within it. The formulation of ferrite is xxFe2O4 where xx represents various metals. For inductor cores soft ferrites are used, which have low coercivity and thus low hysteresis losses. Another similar material is powdered iron cemented with a binder.
Toroidal core inductor[edit]
In an inductor wound on a straight rod-shaped core, the magnetic field lines emerging from one end of the core must pass through the air to re-enter the core at the other end. This reduces the field, because much of the magnetic field path is in air rather than the higher permeability core material. A higher magnetic field and inductance can be achieved by forming the core in a closed magnetic circuit. The magnetic field lines form closed loops within the core without leaving the core material. The shape often used is a toroidal or doughnut-shaped ferrite core. Because of their symmetry, toroidal cores allow a minimum of the magnetic flux to escape outside the core (called leakage flux), so they radiate less electromagnetic interference than other shapes. Toroidal core coils are manufactured of various materials, primarily ferrite, powdered iron and laminated cores.[13]
Choke[edit]
A choke is designed specifically for blocking higher-frequency alternating current (AC) in an electrical circuit, while allowing lower frequency or DC current to pass. It usually consists of a coil of insulated wire often wound on a magnetic core, although some consist of a donut-shaped "bead" of ferrite material strung on a wire. Like other inductors, chokes resist changes to the current passing through them, and so alternating currents of higher frequency, which reverse direction rapidly, are resisted more than currents of lower frequency; the choke's impedance increases with frequency. Its low electrical resistance allows both AC and DC to pass with little power loss, but it can limit the amount of AC passing through it due to its reactance.
Variable inductor[edit]

Probably the most common type of variable inductor today is one with a moveable ferrite magnetic core, which can be slid or screwed in or out of the coil. Moving the core farther into the coil increases the permeability, increasing the magnetic field and the inductance. Many inductors used in radio applications (usually less than 100 MHz) use adjustable cores in order to tune such inductors to their desired value, since manufacturing processes have certain tolerances (inaccuracy). Sometimes such cores for frequencies above 100 MHz are made from highly conductive non-magnetic material such as aluminum.[14] They decrease the inductance because the magnetic field must bypass them.
Air core inductors can use sliding contacts or multiple taps to increase or decrease the number of turns included in the circuit, to change the inductance. A type much used in the past but mostly obsolete today has a spring contact that can slide along the bare surface of the windings. The disadvantage of this type is that the contact usually short-circuits one or more turns. These turns act like a single-turn short-circuited transformer secondary winding; the large currents induced in them cause power losses.
A type of continuously variable air core inductor is the variometer. This consists of two coils with the same number of turns connected in series, one inside the other. The inner coil is mounted on a shaft so its axis can be turned with respect to the outer coil. When the two coils' axes are collinear, with the magnetic fields pointing in the same direction, the fields add and the inductance is maximum. When the inner coil is turned so its axis is at an angle with the outer, the mutual inductance between them is smaller so the total inductance is less. When the inner coil is turned 180° so the coils are collinear with their magnetic fields opposing, the two fields cancel each other and the inductance is very small. This type has the advantage that it is continuously variable over a wide range. It is used in antenna tuners and matching circuits to match low frequency transmitters to their antennas.
Another method to control the inductance without any moving parts requires an additional DC current bias winding which controls the permeability of an easily saturable core material. See Magnetic amplifier.
Circuit theory[edit]
The effect of an inductor in a circuit is to oppose changes in current through it by developing a voltage across it proportional to the rate of change of the current. An ideal inductor would offer no resistance to a constant direct current; however, only superconducting inductors have truly zero electrical resistance.
The relationship between the time-varying voltage v(t) across an inductor with inductance L and the time-varying current i(t) passing through it is described by the differential equation:
When there is a sinusoidal alternating current (AC) through an inductor, a sinusoidal voltage is induced. The amplitude of the voltage is proportional to the product of the amplitude (IP) of the current and the frequency (f) of the current.
In this situation, the phase of the current lags that of the voltage by π/2 (90°). For sinusoids, as the voltage across the inductor goes to its maximum value, the current goes to zero, and as the voltage across the inductor goes to zero, the current through it goes to its maximum value.
If an inductor is connected to a direct current source with value I via a resistance R, and then the current source is short-circuited, the differential relationship above shows that the current through the inductor will discharge with an exponential decay:
Reactance[edit]
The ratio of the peak voltage to the peak current in an inductor energised from a sinusoidal source is called the reactance and is denoted XL. The suffix is to distinguish inductive reactance from capacitive reactance due to capacitance.
Thus,
Reactance is measured in the same units as resistance (ohms) but is not actually a resistance. A resistor will dissipate energy as heat when a current passes. This does not happen with an inductor; rather, energy is stored in the magnetic field as the current builds and later returned to the circuit as the current falls. Inductive reactance is strongly frequency dependent. At low frequency the reactance falls, and for a steady current (zero frequency) the inductor behaves as a short-circuit. At increasing frequency, on the other hand, the reactance increases and at a sufficiently high frequency the inductor approaches an open circuit.
Laplace circuit analysis (s-domain)[edit]
When using the Laplace transform in circuit analysis, the impedance of an ideal inductor with no initial current is represented in the s domain by:
where
 is the inductance, and
is the inductance, and is the complex frequency.
is the complex frequency.
If the inductor does have initial current, it can be represented by:
- adding a voltage source in series with the inductor, having the value:
where
 is the inductance, and
is the inductance, and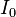 is the initial current in the inductor.
is the initial current in the inductor.
(Note that the source should have a polarity that is aligned with the initial current)
- or by adding a current source in parallel with the inductor, having the value:
where
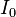 is the initial current in the inductor.
is the initial current in the inductor. is the complex frequency.
is the complex frequency.
Inductor networks[edit]
Inductors in a parallel configuration each have the same potential difference (voltage). To find their total equivalent inductance (Leq):
The current through inductors in series stays the same, but the voltage across each inductor can be different. The sum of the potential differences (voltage) is equal to the total voltage. To find their total inductance:
These simple relationships hold true only when there is no mutual coupling of magnetic fields between individual inductors.
Stored energy[edit]
Neglecting losses, the energy (measured in joules, in SI) stored by an inductor is equal to the amount of work required to establish the current through the inductor, and therefore the magnetic field. This is given by:
where L is inductance and I is the current through the inductor.
This relationship is only valid for linear (non-saturated) regions of the magnetic flux linkage and current relationship. In general if one decides to find the energy stored in a LTI inductor that has initial current in a specific time between  and
and 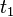 can use this:
can use this:
Q factor[edit]
An ideal inductor would have no resistance or energy losses. However, real inductors have winding resistance from the metal wire forming the coils. Since the winding resistance appears as a resistance in series with the inductor, it is often called the series resistance. The inductor's series resistance converts electric current through the coils into heat, thus causing a loss of inductive quality. The quality factor (or Q) of an inductor is the ratio of its inductive reactance to its resistance at a given frequency, and is a measure of its efficiency. The higher the Q factor of the inductor, the closer it approaches the behavior of an ideal, lossless, inductor. High Q inductors are used with capacitors to make resonant circuits in radio transmitters and receivers. The higher the Q is, the narrower the bandwidth of the resonant circuit.
The Q factor of an inductor can be found through the following formula, where L is the inductance, R is the inductor's effective series resistance, ω is the radian operating frequency, and the product ωL is the inductive reactance:
Notice that Q increases linearly with frequency if L and R are constant. Although they are constant at low frequencies, the parameters vary with frequency. For example, skin effect, proximity effect, and core losses increase R with frequency; winding capacitance and variations in permeability with frequency affect L.
Qualitatively, at low frequencies and within limits, increasing the number of turns N improves Q because L varies as N2 while R varies linearly with N. Similarly, increasing the radius r of an inductor improves Q because L varies as r2 while R varies linearly with r. So high Q air core inductors often have large diameters and many turns. Both of those examples assume the diameter of the wire stays the same, so both examples use proportionally more wire (copper). If the total mass of wire is held constant, then there would be no advantage to increasing the number of turns or the radius of the turns because the wire would have to be proportionally thinner.
Using a high permeability ferromagnetic core can greatly increase the inductance for the same amount of copper, so the core can also increase the Q. Cores however also introduce losses that increase with frequency. The core material is chosen for best results for the frequency band. At VHF or higher frequencies an air core is likely to be used.
Inductors wound around a ferromagnetic core may saturate at high currents, causing a dramatic decrease in inductance (and Q). This phenomenon can be avoided by using a (physically larger) air core inductor. A well designed air core inductor may have a Q of several hundred.
Inductance formulas[edit]
The table below lists some common simplified formulas for calculating the approximate inductance of several inductor constructions.
| Construction | Formula | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical air-core coil[15] | 
|
The exact calculation of K is complex. K is approximately unity for a coil which is much longer than its diameter and is tightly wound using small gauge wire (so that it approximates a current sheet).[16] |
| Straight wire conductor[17] | ![L = \frac{\mu_0}{2\pi} \left(
l \ln\left[\frac{1}{c}\left(l + \sqrt{l^2 + c^2}\right)\right] - \sqrt{l^2 + c^2} +
c + \frac{l}{4 + c \sqrt{\frac{2}{\rho}\omega\mu}}
\right)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/e/f/a/efa2d7d584be0f98d7f29ea5f27764a5.png)
|
Exact if ω = 0 or ω = ∞ |
![L = \frac{1}{5} l \left[\ln\left(\frac{4l}{d}\right) - 1\right]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/6/e/a/6eae9f27f452930f27961b76fdef67f9.png) (when d² f ≫ 1 mm² MHz) (when d² f ≫ 1 mm² MHz)![L = \frac{1}{5} l \left[\ln\left(\frac{4l}{d}\right) - \frac{3}{4}\right]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/2/f/9/2f9d2129afc2623a650fc45b5271a686.png) (when d² f ≪ 1 mm² MHz) (when d² f ≪ 1 mm² MHz)
|
|
|
| Short air-core cylindrical coil[21] | 
|
|
| Multilayer air-core coil[22] | 
|
|
| Flat spiral air-core coil[23][citation needed] | 
|
|
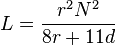
|
accurate to within 5 percent for d > 0.2 r.[24] | |
| Toroidal core (circular cross-section)[25] | 
|
|
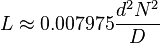
|
approximation when d < 0.1 D | |
| Toroidal core (rectangular cross-section)[24] | 
|
See also[edit]
- Gyrator – a network element that can simulate an inductor
- Induction coil
- Induction cooking
- Induction loop
- RL circuit
- RLC circuit
- Magnetomotive force
- Reactance (electronics) – opposition to a change of electric current or voltage
- Saturable reactor – a type of adjustable inductor
- Solenoid
Notes[edit]
- ^ Singh, Yaduvir (2011). Electro Magnetic Field Theory. Pearson Education India. p. 65. ISBN 8131760618.
- ^ Wadhwa, C. L. (2005). Electrical Power Systems. New Age International. p. 18. ISBN 8122417221.
- ^ Pelcovits, Robert A.; Josh Farkas (2007). Barron's AP Physics C. Barron's Educatonal Series. p. 646. ISBN 0764137107.
- ^ a b c Purcell, Edward M.; David J. Morin (2013). Electricity and Magnetism. Cambridge Univ. Press. p. 364. ISBN 1107014026.
- ^ "Aircraft electrical systems". Wonderquest.com. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
- ^ "An Unassuming Antenna - The Ferrite Loopstick". Radio Time Traveller. January 23, 2011. Retrieved March 5, 2014.
- ^ Frost, Phil (December 23, 2013). "What's an appropriate core material for a loopstick antenna?". Amateur Radio beta. Stack Exchange, Inc. Retrieved March 5, 2014.
- ^ Poisel, Richard (2011). Antenna Systems and Electronic Warfare Applications. Artech House. p. 280. ISBN 1608074846.
- ^ Yadava, R. L. (2011). Antenna and Wave Propagation. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. p. 261. ISBN 8120342917.
- ^ Vishay. "Products - Inductors - IHLP inductor loss calculator tool landing page". Vishay. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
- ^ View: Everyone Only Notes. "IHLP inductor loss calculator tool". element14. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
- ^ "Inductors 101" (PDF). vishay. Retrieved 2010-09-24.
- ^ "Inductor and Magnetic Product Terminology" (PDF). Vishay Dale. Retrieved 2012-09-24.
- ^ http://www.coilcraft.com/pdfs/uni5.pdf Coilcraft catalog page with aluminum cores. Accessed 10 July 2015.
- ^ a b Nagaoka, Hantaro (1909-05-06). "The Inductance Coefficients of Solenoids" (PDF) 27. Journal of the College of Science, Imperial University, Tokyo, Japan: 18. Retrieved 2011-11-10.
- ^ Kenneth L. Kaiser, Electromagnetic Compatibility Handbook, p. 30.64, CRC Press, 2004 ISBN 0849320879.
- ^ Rosa, Edward B. (1908). "The Self and Mutual Inductances of Linear Conductors" (PDF). Bulletin of the Bureau of Standards 4 (2): 301–344. doi:10.6028/bulletin.088
- ^ Rosa 1908, equation (11a), subst. radius ρ = d/2 and cgs units
- ^ Terman 1943, pp. 48–49, convert to natural logarithms and inches to mm.
- ^ Terman (1943, p. 48) states for l < 100 d, include d/2l within the parentheses.
- ^ ARRL Handbook, 66th Ed. American Radio Relay League (1989).
- ^ Wheeler, H.A. (October 1928). "Simple Inductance Formulas for Radio Coils". Proceedings of the Institute of Radio Engineers 16 (10): 1398. Retrieved 22 June 2015.
- ^ For the second formula, Terman 1943, p. 58 which cites to Wheeler 1928.
- ^ a b Terman 1943, p. 58
- ^ Terman 1943, p. 57
References[edit]
- Terman, Frederick (1943). "Radio Engineers' Handbook". McGraw-Hill
- Wheeler, H. A. (October 1928). "Simple Inductance Formulae for Radio Coils". Proc. I. R. E. 16 (10): 1398. doi:10.1109/JRPROC.1928.221309
External links[edit]
| The Wikibook Electronics has a page on the topic of: Inductors |
| Look up inductor in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Inductors. |
- General
- How stuff works The initial concept, made very simple
- Capacitance and Inductance – A chapter from an online textbook
- Spiral inductor models. Article on inductor characteristics and modeling.
- Online coil inductance calculator. Online calculator calculates the inductance of conventional and toroidal coils using formulas 3, 4, 5, and 6, above.
- AC circuits
- Understanding coils and transforms
- Bowley, Roger (2009). "Inductor". Sixty Symbols. Brady Haran for the University of Nottingham.
- Inductors 101 Instructional Guide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
















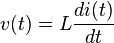

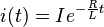



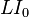


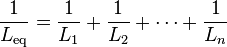

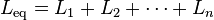



 × 10−7 H/m
× 10−7 H/m